The Key Differences Between AC and DC EV Chargers
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more prevalent, the demand for efficient and convenient charging solutions has soared. Two primary types of EV chargers are available in the market: Alternating Current (AC) chargers and Direct Current (DC) chargers. Each type has its unique advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications. This article aims to explore what AC and DC EV chargers are, highlight their differences, and guide you in selecting the right charger for your needs.
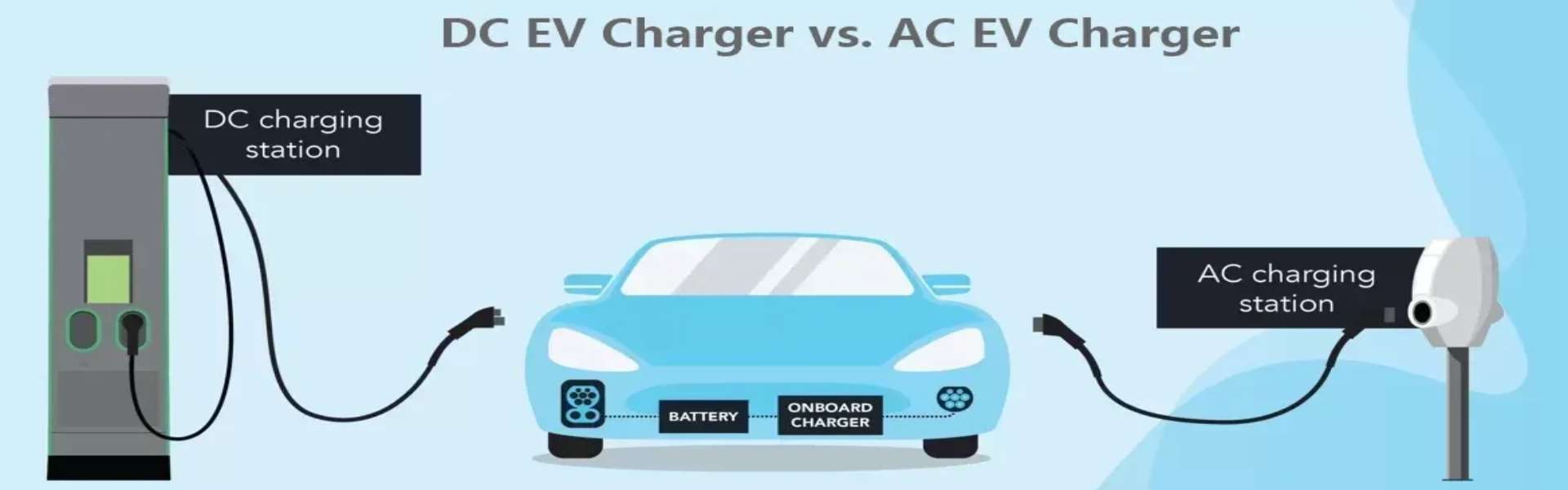
What is an AC EV Charger?
AC, or Alternating Current, is an electrical current where the flow of charge periodically changes direction. AC power is widely used because it can be efficiently transmitted over long distances, forming the backbone of modern power grids. Renewable energy sources such as wind and hydropower generate AC power, enhancing its versatility.
In EV charging, AC chargers are typically found in residential settings and public charging stations. These chargers draw AC power from the grid and deliver it to the vehicle's onboard charger, which converts it to DC power to charge the battery. Due to this conversion process, AC chargers generally have slower charging speeds. However, their lower power output makes them ideal for overnight charging or scenarios where the vehicle will be stationary for extended periods.
What is a DC EV Charger?
In contrast, DC, or Direct Current, is an electrical current that flows in a single direction. DC power is commonly generated by renewable energy sources like solar panels. This unidirectional flow of electricity makes DC suitable for energy storage systems, electronics, and LED lighting.
DC EV chargers bypass the vehicle's onboard charger and deliver DC power directly to the battery. This direct delivery results in much faster charging times compared to AC chargers. DC chargers are often found in commercial and industrial settings, such as highway rest stops, where drivers need quick recharges to continue their journey. However, due to their higher power output and advanced technology, DC chargers are more expensive to install and maintain.
Key Differences Between AC and DC EV Chargers
Charging Speed
- AC Chargers: Typically have slower charging speeds because the AC power from the grid must be converted to DC power by the vehicle's onboard charger. This conversion limits the power delivered to the battery, resulting in charging times ranging from several hours to overnight.
- DC Chargers: Provide much faster charging speeds by delivering DC power directly to the battery. In some cases, a DC charger can provide an 80% charge in as little as 20-30 minutes.
Cost and Installation
- AC Chargers: Generally more affordable to purchase and install. They can be connected to a standard electrical outlet and are commonly used in residential settings.
- DC Chargers: More expensive due to their advanced technology and higher power output. They require specialized equipment and infrastructure, making them more suitable for commercial and industrial use.
Use Cases
- AC Chargers: Ideal for situations where the vehicle will be parked for an extended period, such as overnight at home or during the workday. They provide a steady and reliable charge sufficient for most daily driving needs.
- DC Chargers: Best suited for scenarios requiring fast charging, such as long road trips or commercial fleets needing quick recharges between shifts.
Energy Efficiency
- AC Chargers: Generally more energy-efficient for home and small-scale use, designed to work with existing electrical infrastructure. However, slower charging speeds may result in higher overall energy consumption if the vehicle is frequently charged.
- DC Chargers: While faster, they may have slightly lower energy efficiency due to higher power output and potential energy loss during conversion. The convenience of fast charging often outweighs this trade-off, especially in commercial settings.
How to Choose the Right Charger?
Choosing between an AC and DC EV charger depends on factors such as charging needs, budget, and intended use. Considerations include:
- Daily Driving Habits: An AC charger is sufficient if you drive short distances daily and can charge overnight.
- Charging Frequency: A DC charger is more appropriate if you need multiple daily charges or quick turnarounds.
- Location: For home use, an AC charger is typically best due to lower cost and simpler installation. DC chargers are more suitable for public charging stations or commercial settings.
- Budget: AC chargers are more affordable, making them an excellent choice for most EV owners. If you have the budget and need for fast charging, investing in a DC charger could be worthwhile.
- Long-Term Plans: Consider future charging needs. If faster charging is anticipated, investing in a DC charger now may be beneficial, even if an AC charger meets current needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between AC and DC EV chargers is crucial for selecting the right charger for your needs. AC chargers offer a cost-effective and convenient solution for regular, slow charging, ideal for home use. DC chargers, with their rapid charging capabilities, are better suited for commercial settings or situations requiring fast charging. By choosing the right charger, you can align your charging solution with your lifestyle and driving habits.

